Soil fertility is a key factor in successful farming.
The quality of the soil determines the yield, growth and development of plants.
Determining soil fertility is an important step for any gardener or farmer.
There are several methods available to assess the potential of land for growing plants.
Visual assessment
The first step in determining soil fertility is a visual inspection. Fertile soil is usually dark in color, ranging from dark brown to black.
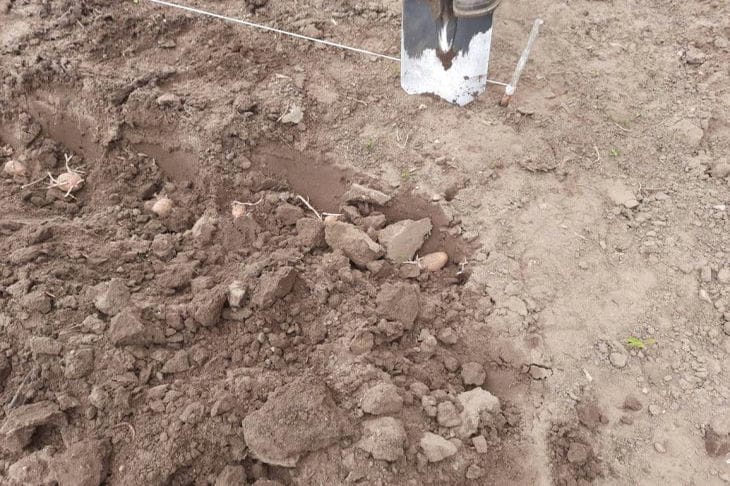

This is due to the high content of humus, an organic substance that plays a key role in plant nutrition. Light, sandy or clay soils are generally less fertile.
The structure and texture of the soil are also important. Fertile soil should be loose, crumble easily in the hands, but retain its shape when compressed.
If the soil is too compact or, on the contrary, crumbles like sand, this may indicate fertility problems.
Check for the presence of living organisms
Fertile soil is a whole ecosystem full of life. The presence of earthworms, insects and other small organisms is a good sign.
Earthworms are especially important because they break down organic matter and improve soil structure.
A simple test: dig a small hole about 30 cm deep and see if there are any living organisms in it.
Water retention capacity test
Fertile soil should retain moisture well, but not be waterlogged. A simple test: take a handful of soil and squeeze it in your fist.
If, when you open your palm, the earth retains its shape, but crumbles easily when touched, this is a good sign.
If the soil remains dry and crumbly or, conversely, too wet and sticky, this may indicate problems with water-holding capacity.
Checking the pH of the soil
Soil pH is an important indicator of its fertility. Most plants prefer neutral or slightly acidic soil (pH 6.0-7.0).
To determine the exact pH, you can use special testers available in gardening stores. An alternative method is to use vinegar and baking soda. If the soil fizzes when vinegar is added, it is alkaline. If it fizzes when baking soda and water are added, it is acidic.
Organic Matter Test
A high organic content is a sign of fertile soil. A simple test: place a handful of soil in a transparent container with water, stir and let settle.
Organic matter will float on the surface or form a top layer of sediment. The larger this layer, the more organic matter there is in the soil.
Plant growth assessment
Monitoring plant growth is one of the most reliable ways to assess soil fertility.
Healthy, strong plants with bright foliage and abundant flowers indicate good soil quality. Plants that are stunted, pale-leaved, or growing poorly may indicate fertility problems.
Laboratory analysis
To obtain the most accurate and complete information about the condition of the soil, it is recommended to conduct a laboratory analysis.
It allows you to determine the content of essential nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium), microelements, pH and other important characteristics. Based on the results of the analysis, you can develop an optimal strategy for fertilizing and improving the soil.
Seasonal changes
It is important to remember that soil fertility can vary depending on the season and weather conditions.
In the spring, after the snow melts, the soil may be wetter and richer in nutrients. In the summer, especially in hot weather, the topsoil may dry out and lose some of its properties. Therefore, it is better to evaluate fertility several times during the growing season.